Abstract
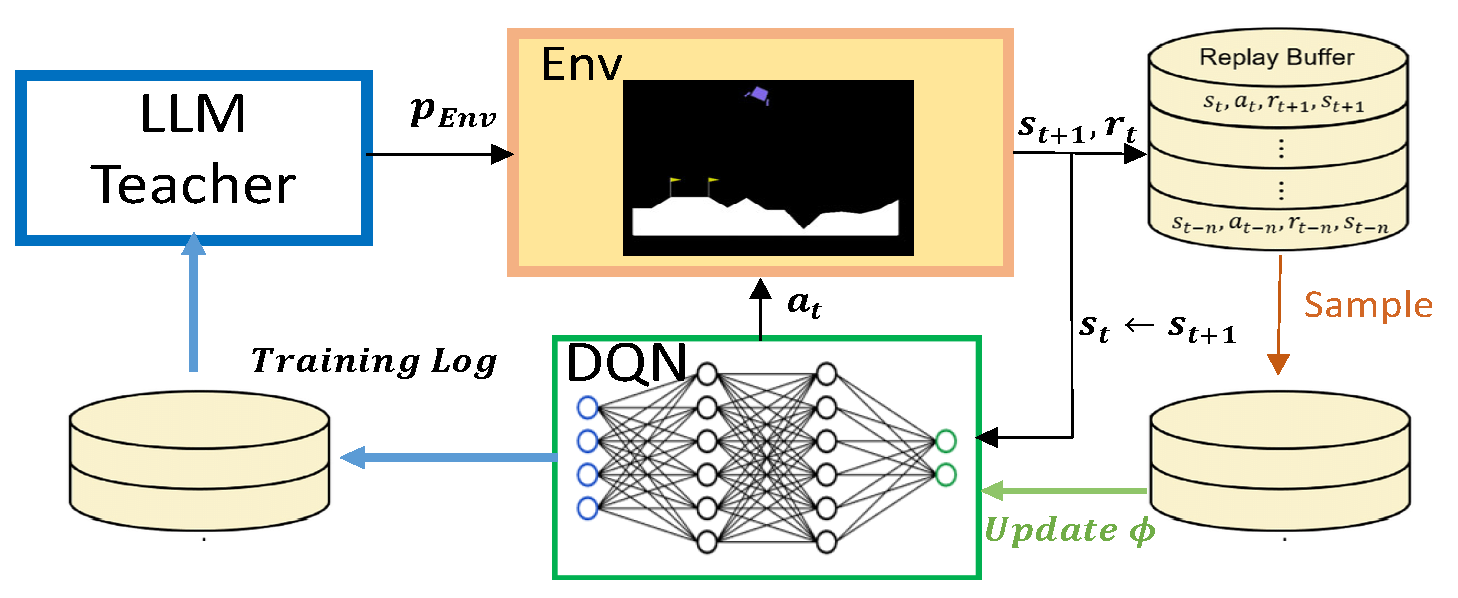
In this work, we present a novel approach to automatic curriculum learning (ACL) using Large Language Models (LLMs) named ACL-LLM to enhance the performance and learning efficiency of reinforcement learning agents. The ACL-LLM algorithm aims to leverage the capabillities of LLMs to reduce human effort and intervention in the training process, ultimately improving the generalization capabilities of reinforcement learning agents.
Our approach was implemented in the LunarLander-V2 environment utilizing a Deep Q-Network (DQN) agent and OpenAI GPT3.5-Turbo Model APl as the base models for the two key components of our algorithm. The LLM teacher was tasked with generating and modifying the environmental parameters, such as gravity, wind power, and turbulence power to facilitate the learning process of the DQN agent during training time by determining whether to alter the environment’s difficulty based on the agent’s performance metrics.
To test our approach, we trained two different models and tested them on test environments generated from uniformly sampled environment parameters. The first model was trained using a DQN agent on a set of environments generated by ACL-LLM. The second model was trained using a DQN agent the same set of environments used for the first model but in a randomized order.
We observed that the ACL-LLM algorithm significantly improved the learning efficiency and robustness of the agents when training with limited steps and resources. ACL-LLM could offer a substantial advantage in tasks where training or sampling is expensive, enhancing agent generalizability through an automatically generated curriculum. However, in experiments with sufficient training steps, the advantages of the proposed algorithm diminished as the task was not complex and both agents converged.